Crystals in Urine: Acidic Urine
Crystals
Formation and appearance
of crystals in urine depends
upon pH of the urine, i.e.
acidic or alkaline.
Crystals
in Acidic Urine
These are as under :
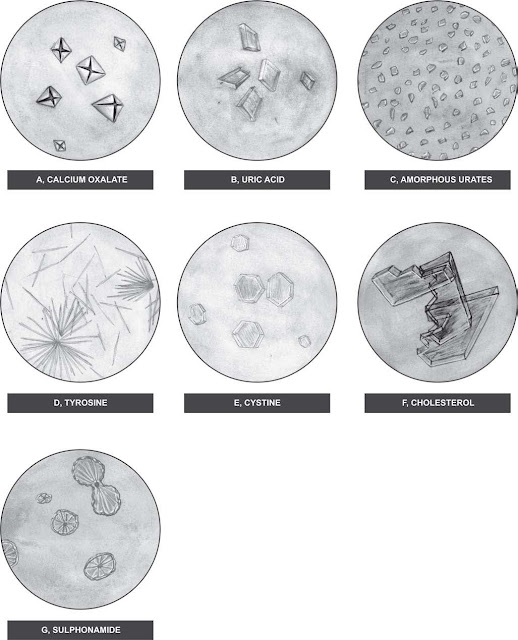
i. Calcium oxalate
ii. Uric acid
iii. Amorphous urate
iv. Tyrosine
v. Cystine
vi. Cholesterol crystals
vii. Sulphonamide
i) Calcium Oxalate
These are colourless
refractile and have octahedral
envelope-like structure.
They can also be dumb-bell
shaped
ii) Uric Acid
They are yellow or brown
rhomboid-shaped seen singly
or in rosettes. They can
also be in the form of prism,
plates and sheaves
iii) Amorphous Urate
They appear as yellowish
brown granules in the form of
clumps. They dissolve on
heating. When
they are made of sodium
urate, they are needle-like in
the form of thorn-apple.
They are passed more often in
patients having gout.
iv) Tyrosine
They are yellowish in the
form of silky needles or sheaves
.They are passed in urine in
jaundice.
v)
Cystine
They are colourless,
hexagonal plates which are highly
refractile .They are passed
in urine in an
inborn error of metabolism,
cystinuria.
vi)
Cholesterol Crystals
These are rare and are seen
in urinary tract infection,
rupture of lymphatic into
renal pelvis or due to blockage
of lymphatics
vii)
Sulphonamide
They appear as yellowish
sheaves, rosettes, or rounded
with radial striations .They
appear in urine
after administration of
sulphonamide drugs.
Comments
Post a Comment